A marketing plan is a basic document that describes specific steps and actions to achieve the set of marketing goals for a certain period of time. As a rule, a marketing plan is drawn up for a year (but there may be other options, for example, 3 months, six months, etc.) and should correspond to the general direction of the company’s development and its main goals.
There are different structures for drawing up a marketing plan, it depends, first of all, on the size of the companies and the goals set.
Let’s briefly consider the main elements of the marketing plan, for this purpose we will conditionally allocate three blocks.
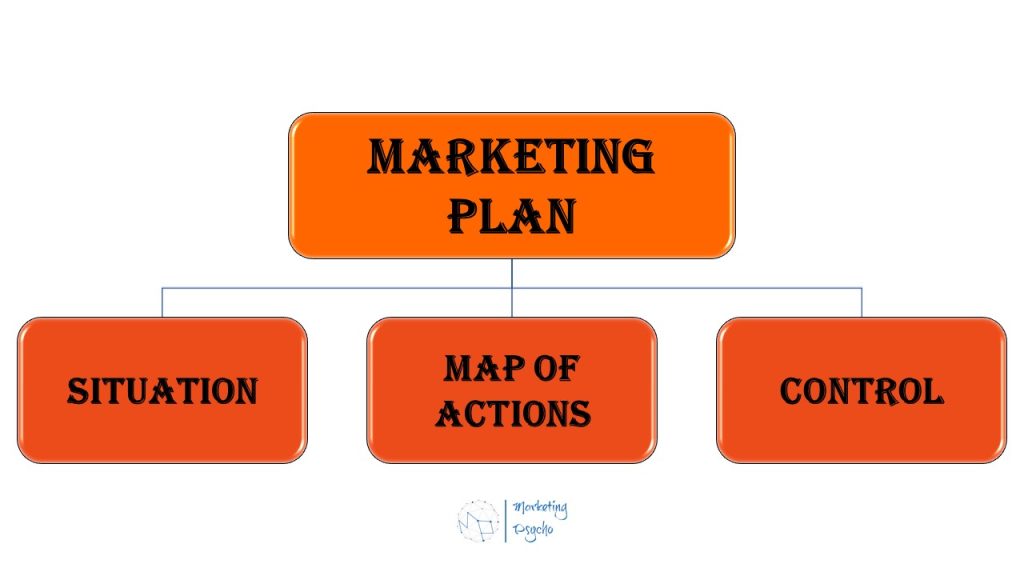
Description of the Situation
Before you start moving, you need to understand where you are. To do this, you need to analyze the environment around you.
This block includes the following:
- Basic information about the company
- who are you (name, form of ownership, location)
- who are your top managers
- what do you offer (what is your product/service)
- your value proposition – this is the value that your customer will receive when they use your product or service
- Situation Analysis
Situation analysis is carried out to determine the external and internal situation in which the company is currently located. If you are a small company, the analysis may include only the key elements that are necessary to describe the current situation. If you are a large or medium-sized organization, then in this case you have more resources and opportunities to conduct a detailed situation analysis, which usually includes the following:
Analysis of the External Environment
- Macro Environment Analysis
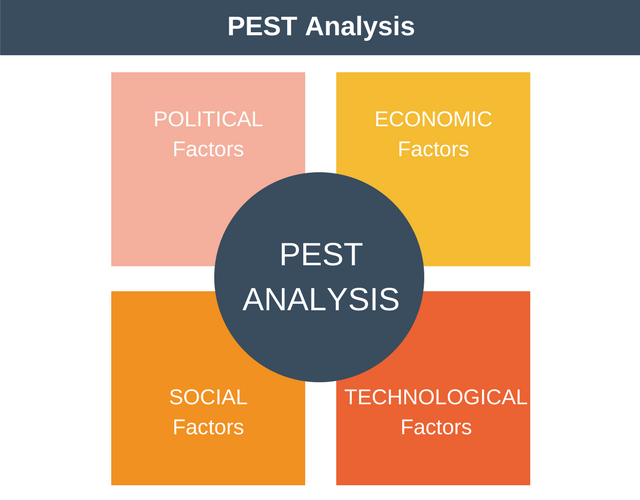
PEST analysis is a simple and convenient method for analyzing the macro environment of an enterprise. PEST is an abbreviation of the following words: Political, Economic, Sociocultural and Technological. The most common variation of PEST analysis is PESTEL analysis. PESTEL analysis includes two more indicators: legal factors (L – Legal) and environmental factors (E – Environmental or Ecological).
Who are your main competitors, their weaknesses and strengths, their position in the market at the moment, promotion strategy, etc. In the same block, you can use Porter’s five forces analysis methodology.
- Market Analysis
What is your market (size, trends, profitability, growth rates, market segmentation)
- Suppliers and Distributers Analysis
The following characteristics are important for suppliers: the cost of the goods, quality, delivery schedule. For distributors: distribution channels, distribution chain, sales volume, etc.
- Target Audience Analysis
Who your current and future clients are, their interests, demographic and psychographic features and go on, their location. You can compose a customer profile and also determine the reasons for purchasing behavior (why the customer prefers to buy this product rather than another one).
Analysis of the Internal Environment
This section also can be called the company’s analysis, since it includes an assessment of the company’s capabilities, aimed at determining the current state of the business, its strengths and weaknesses, and identifying strategic problems. This category may include the following types of analyses:
- Company goals: mission statement, vision statement, financial, long-term, etc.
- Marketing strategy: product, price, promotion, distribution.
- Resources: people, finance, information, technology and so on.
- Image on the market
- Corporate culture
At this stage, you can use the following methods: 5Cs Analysis, ABC Analysis, XYZ Analysis, etc.
- After conducting a Situation Analysis using the method you have chosen, you need to make a SWOT analysis to clearly describe the results.
Map of Action
Map of action is your detailed plan of what you want to do. When you clearly understand what situation you are in, you need to set goals correctly. Goals is what you want to achieve after completing the marketing plan. Goals should correspond to the main business objectives of the company. One business objective can correspond to several marketing goals. For example, the main business objective is to create a strong brand.
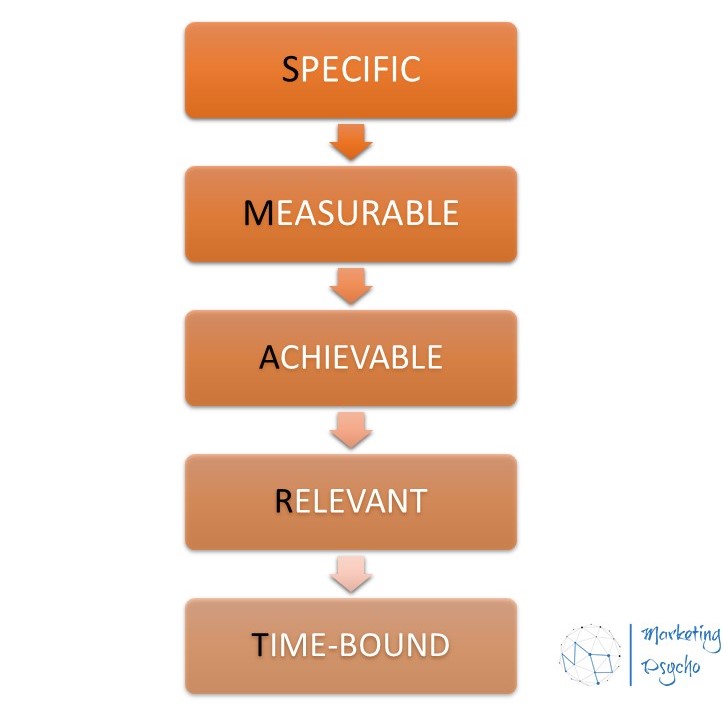
Marketing goals for the fulfillment of this business objective can be the following: increase brand awareness by 20%, increase brand loyalty by 20%, etc. For goals, you need to set a specific time period, it depends on the time of execution of your plan. For successful goal setting, you can use the SMART methodology. SMART is a methodology used to define goals and set tasks. There are various ways to decipher the abbreviation SMART. The most well-known interpretations: SMART is Specific, Measurable, Achievable/Assignable, Relevant/Realistic, and Time-bound/Time-limited.
When you have identified a goal, you should draw up a detailed action plan for achieving them based on the agreed budget. You can include the following items in it:
- Actions (What) – what exactly needs to be done to achieve the set goals;
- Time (When) – in what time frame it is necessary to carry out the activities;
- Responsible (Who) – who will be responsible for the implementation of a specific action;
- Performance indicators – benchmarks are needed to understand what you have achieved;
- Budget (How much) – how much it will cost.
The action plan can be presented in the form of such a table:
| Actions (What) | Time (When) | Responsible (Who) | Performance indicators | Budget (How much) |
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. |
Control and Measure
You should monitor the indicators that have been set in your action plan to take corrective measures in time. If your plan deviates from the intended goals, then you need to change it. The structure of your marketing plan should be agile and adapt to the changed situation.
This article lists the main elements of a marketing plan. But it is worth noting that you are creating this document for it to help you in your work, to organize your activities and increase efficiency, so, of course, you can change the structure of the plan so that it corresponds to your individual approach. Experiment, expand items, add detailed information, if necessary, to achieve your goals. Or, on the contrary, shorten, leave only the main information so as not to be distracted by additional factors.