Competition in the market is one of the key concepts in the economy. First of all, competition is rivalry. It is rivalry that helps companies not to stand still and move forward, improving their positions. Therefore, you need to pay special attention to this area. To always be up to date, you must constantly monitor your competitors, this applies to both existing and potential ones. You should study the main players in the market in detail to finally understand their weaknesses and strengths, this will help you improve the efficiency of your company. Also, in the competitive analysis, we should determine our place in the market in relation to competitors, this will give us an understanding of where to go next and what needs to be done for this.
Competitive Analysis Based on Comparison
One of the most common methods of conducting competitive analysis is comparison. This is a logical method of competitive analysis, the point is you make a list of competitors and criteria by which you will then compare them, and then draw conclusions based on this data. It is possible to distinguish the main stages of its implementation:
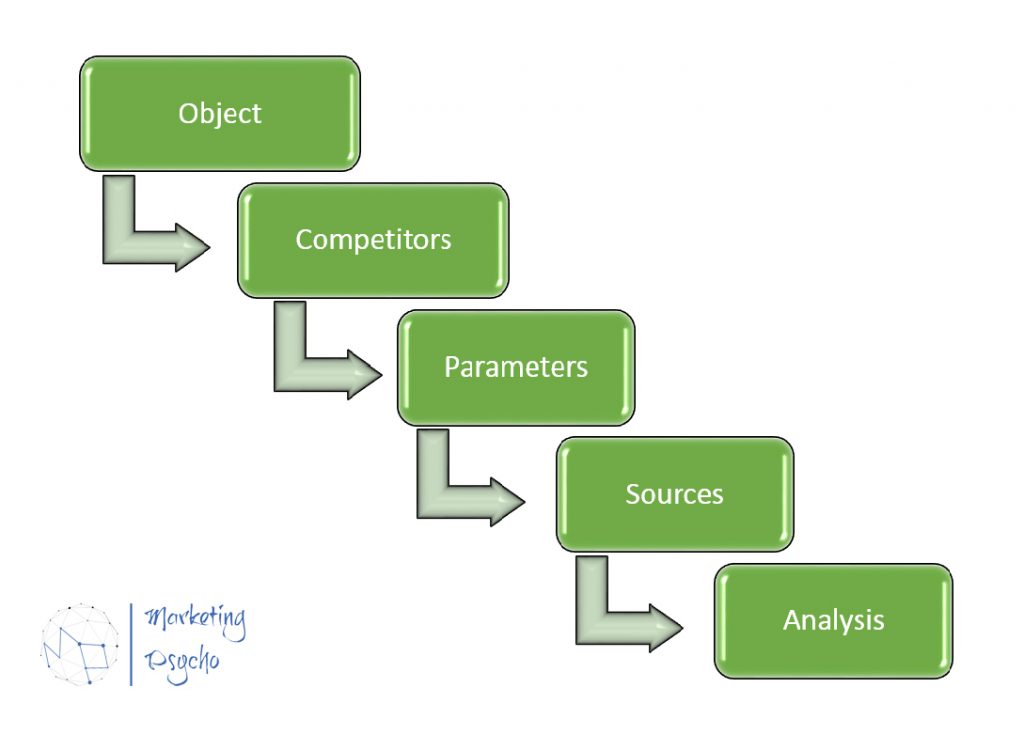
Object
At this stage, we define the main idea of the study in total: why we conduct it (the goal) and general positions. To do this, you can describe the situation of the industry as a whole, the state of the market, the current situation in which your company is located, external factors that affect both the industry and your company, the problems that the organization has faced and that need to be solved with the help of this study.
Competitors
In this section, we compile lists of competitors. There are different approaches to selecting competitors for analysis.
Competitors can be divided into the following groups:
- direct competitors are companies that offer exactly the same or similar products or services that work with you in the same market, aimed at the same segment of consumers. Direct competitors represent the most serious competition for you, as they can entice your customers with various loyalty programs, lower prices, more favorable terms of cooperation, etc.,
- indirect competitors are companies that offer a substitute product but work for the same target audience. Indirect competitors also pose a threat to you, although on a smaller scale than direct competitors. First, they attract some of your customers, and, secondly, they can become direct competitors for you in the future.
- prospective competitors are companies that may pose a threat to you in the future. This type of competition is quite unpredictable, so it is difficult to track them and predict the next steps. These can be:
- Existing companies that are not yet in your market, but that may appear at any time
- Indirect competitors
- A company that can offer a solution to the problem for consumers that is different from your product
Another option for making a list of competitors is based on the number of participants.
- complete list. In this case, you list all the competitors. This is quite a time-consuming path since most companies have a huge number of competitors, so you will have to collect and process too much information. This approach is preferred for companies that have a small number of competitors.
- incomplete list. It is compiled depending on the research objectives, for example, the following areas can be distinguished:
- key players. Lists the main companies in the market that are the driving force in this industry and can be an example of successful solutions and strategies. Here we can talk about such a concept as benchmarking. Benchmarking is the ability to find or identify best practices and techniques that other firms use, to study them, and apply them to your business.
- the closest competitors are competitors operating in the geographical areas of the market that are close to you in terms of position.
- three main competitors. You can limit your list by highlighting your top three competitors.
Whatever method you choose to compile the list (suggested in this article or your own), it should in any case meet your needs and research goals.
Parameters
In accordance with this section, you define the criteria by which you will compare competitors and your company. The criteria are also selected individually for each company, based on the set research goals. You can select the following parameters and analyze them separately, for example, price, quality, quantity, product/service promotion activities, customer service, brand awareness/loyalty, market share, distribution, technology, personnel, target audience, etc.
You can group the criteria and use the key success factors (KSFs). KSFs are the main indicators by which a firm has an advantage.
For example:
- technological factors
- production factors
- distribution
- marketing
- personnel factors and other types of KSFs
Sources
At this step, you define the sources of information. The sources of information are usually divided into primary and secondary.
A primary source gives you direct access to the subject of your research. Primary sources can either be qualitative or quantitative data that you collect yourself (It can be observations, interviews and surveys, experiments) or sources produced by people directly involved in the topic (recordings of speeches, social media posts, letters, and others).
Primary information is reliable and authentic, but it is quite an expensive type of information collection and takes a lot of time.
Secondary sources describe, summarize, or discuss information or details originally presented in another source. This type of source is designed for a broad audience. Sources of secondary information collection can be articles in magazines and newspapers; advertising, presentations, promotional materials, etc.; consumer reviews, reviews of former employees of companies; website; online search; your sales department, and so on.
To get more complete information about competitors, you need to use all available sources of information.
Analysis
At this phase, you analyze the data and create a report with conclusions and suggestions.
For the convenience and clarity of the competitive analysis, you can create a table in which you will mark the received data. You can use a scoring system or a descriptive system for evaluating criteria.
The table can look like this, but you can also create your own according to your needs:
| Characteristic 1 | Characteristic 2 | Characteristic 3 | Characteristic 4 | |
| Competitor 1 | ||||
| Competitor 2 | ||||
| Competitor 3 | ||||
| Your company |
When the data is collected and organized, you can also create graphs and charts.
One of the tools for data analysis is the SWOT analysis, in which you list the weaknesses and strengths of your competitors, based on which you will see the further direction of your business development.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Speaking of competitive analysis, it is impossible not to mention Porter’s five forces analysis. This methodology focuses on the industry as a whole, not on its individual part or a set of industries. One industry is characterized by one of Porter’s five forces analysis.
Porter’s five forces analysis is a method of analyzing competition that helps determine the attractiveness of an industry and the profitability of doing business in it. This model was developed by the American expert in the field of economics Michael E. Porter in 1979.
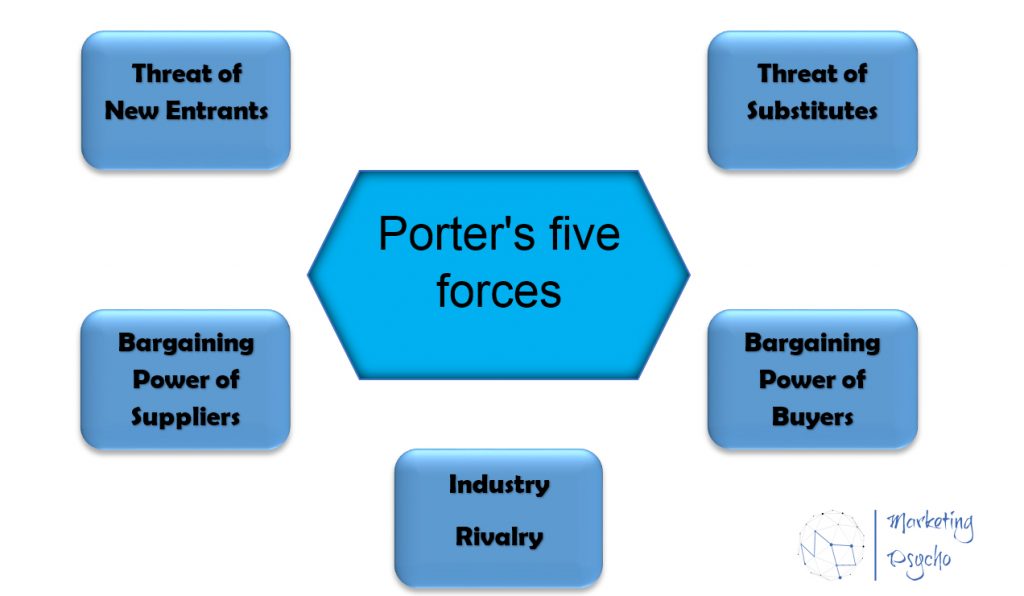
Michael Porter identifies five driving forces in the market.
Threat of New Entrants
These are external potential competitors. New players open up new opportunities, they can offer innovative solutions for this market, use new technologies and resources, this can lead to changes in consumer behavior and reduce the income level of existing market participants. There are constraints for new players to enter this market. First of all, these are barriers to entry. According to M. Porter, barriers to entry include supply-side economies of scale; demand-side benefits of scale; customer switching costs; capital requirements; incumbency advantages independent of size; unequal access to distribution channels; government policy. If the barriers to entry are high, it will be more difficult for new entrants to enter this business sector, and vice versa.
Threat of Substitutes
Substitute products are similar products produced for the same consumers, similar in purpose and use, but with any differences in characteristics. Substitute products affect the price level, so they usually offer a cheaper option for the consumer, for example, due to a different production technology or the use of cheaper raw materials. The price falls, which leads to lower profits. The more attractive the price-quality ratio in substitute products, the greater the threat to the profits of companies that exist in this market. To counter this threat, it is necessary to develop a clear policy of differentiation, focus on the additional advantages of the product, and have a strong brand.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
These are the owners of resources to produce goods in the industry. This includes raw materials, components, labor, maintenance, etc. If suppliers provide a rare product or service, they may have an impact on the company with which they cooperate (refusal of deliveries, inflated prices, unfavorable terms of transactions, etc.).
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Consumers ensure the existence of the market. They can affect competition in the market due to high requirements for the quality of products or services, which, in turn, affects the profits of companies, as the manufacturer increases its costs to improve quality. Buyers are directly connected with the price, as they want to reduce their costs, so they are constantly looking for more favorable offers. The power of buyers is high if they have a large choice and therefore decreases if the number of alternatives decreases. Companies often introduce loyalty programs to retain or attract customers.
Industry Rivalry
Here, the fight unfolds between existing competitors in this market. Thanks to this competition, companies increase advertising and promotion costs, apply different pricing strategies, develop new technologies and solutions, which leads to a decrease in the profitability of the industry.
Profitability in the market depends on the strength of the influence of competitive forces: the stronger the influence, the smaller your profit will be, and the weaker the influence, the more likely you are to get a higher profit. Thanks to the conducted research of the industry, your company will be able to find a suitable niche in the market, the influence of competitive forces in which will be minimized.
Competitive Profiling
In our article, we would also like to pay attention to another option for conducting competitive analysis – competitive profiling. Competitive profiling is the creation of a detailed portrait of competitors for a deeper understanding of their business. As a rule, it includes:
- General description of the competitor company. History, main milestones, location, ownership and organizational structure, company leaders and management, mission and vision of the organization, the unique value proposition (UVP), financial indicators, and more.
- Production. Factory capacity, technology, equipment, production culture, and more.
- Products. Existing product portfolio and product line width, new products, products in development. Patents, intellectual property, know-how. The quality of products, the number of products (volume). Packaging, design.
- Brand. Brand awareness, brand loyalty.
- Marketing:
– Promotion and positioning
- advertising campaigns: advertising in the media (TV, radio, periodicals, Internet), outdoor advertising, indoor advertising, social advertising, etc.
- various types of sales promotion: contests, lotteries, loyalty programs, etc.
- participation in exhibitions, presentations, etc.
– Distribution (analysis of channels: intermediaries (wholesaler, retailer, agent), direct deliveries, channel mix), and more.
– Prices (discounts and sales, price mark-ups)
– Segmentation, target audience, geographical coverage, and so on
– Customer service: pre-sale service, service during the sale, and after-sales service.
- Personnel: number of employees, key employees, core competencies, leadership style, benefits, corporate programs, training, and so on.
You can also add other data to your profile. The more data you have about your competitors, the clearer you will see the overall picture of the business.
The importance of competitive analysis is very great, it allows you to learn the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, to study their strategy, goals, which will allow your company to improve the effectiveness of its actions, so it should become a necessary tool for your business.
To find more marketing analysis tips go to Marketing Analysis section of the website.