Last week I shared with you the second part of Marketing 4.0 book. The third part describes the basic tactics of marketing 4.0. This part covers human-centric marketing, content marketing, the use of omnichannel marketing and engagement marketing.
Human-Centric Marketing
In marketing 4.0 the brand should be aimed at the person, the companies should become a part of the consumer’s life. The brand must demonstrate human qualities, which can attract consumers and contribute to the creation of interpersonal communications.
To understand human nature, the authors advise to turn to digital anthropology. Digital anthropology studies how people interact with a digital interface, how they behave in the face of technology, and how they use technology to interact with each other. Digital anthropology is also used to understand how people perceive brands in their digital communities and what attracts people to certain brands.
Several well-known techniques currently used by marketers include social listening, netnography, and empathic research.
Social listening
The process of monitoring what is said online about a brand, especially in social networks and online communities. This allows you to identify potential buyers, respond to feedback and understand the market and its participants.
Netnography
This ethnography focused on the Internet, was developed by Robert Kozinets, is a method which adapts ethnographic techniques to understand human behavior in online groups or online communities.
Emphatic research
Empathic research is a method that is based on immersion in the community to identify the hidden needs of customers.
According to Stephen Simpson’s book “Leaders without Titles”, leaders have 6 distinctive qualities: physicality, intellectuality, sociability, emotionality, personability, morality.
Physicality
Physical attractiveness has a big impact on people. For brands, the external appeal may be in their distinctive features, such as logos, website, corporate identity, slogans.
Intellectuality
Intellectuality is a person’s ability to possess the knowledge, thinking and the ability to generate ideas. Brands with powerful intelligence are innovative and can launch products and services that neither competitors nor customers could have guessed.
Sociability
Sociable brands listen to customers and also participate in discussions with their consumers. They answer questions and complaints and solve consumer problems. Brands also engage their customers in dialogue.
Emotionality
People who can emotionally communicate with others and control their actions are very influential. Brands that cause emotion in people can encourage a favorable attitude of the customers.
Personability
People with individuality understand what they are good at. Brands with a strong personality also know exactly what they are. But these brands are also not afraid to show their flaws and take full responsibility for their actions.
Morality
Morality characterizes the morality and integrity of the individual. Brands with strong moral qualities are valuable. They ensure that appropriate ethical considerations become a key part of all business decisions. Brands are honest with their consumers.
Brands need to adopt human qualities to attract customers in the human-centric era.
Content marketing
Content marketing, as defined by the authors, is a marketing approach that consists of creating, copying, distributing and expanding content that is interesting, relevant and useful for a certain audience, which will entail its development.
Instead of distributing promotional messages, marketers should distribute content that is useful and meaningful to customers. Unlike traditional advertising, it does not show the benefits of brands but helps people solve their problems.
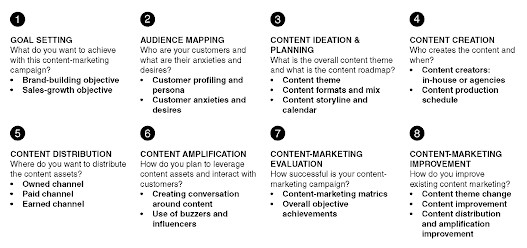
Step by Step Content Marketing
Goal setting
To understand how to create content and how to distribute it, you need to clearly set measurable goals. What do you want to achieve with this content marketing campaign? There are two types of goals in content marketing:
- brand-building objective – increase brand awareness, brand association, and brand loyalty/advocacy.
- sales-growth objective – attracting potential customers, closing a deal, selling related products, raising the number of sales and affiliate programs.
Audience mapping
Who are your customers and what are their anxieties and desires?
- customer profiling and persona
- customer anxieties and desires
A clear understanding of your audience will allow you to identify topics for content that will be useful and interesting.
Content ideation & planning
What are the overall content themes and what is the content roadmap?
- theme content
- content formats and mix
- content storyline and calendar
At this stage, you have to determine the appropriate content format for the selected audience. Content should be relevant to the concerns and challenges of consumers.
Content creation
Who creates content and when? It is necessary to define:
- how will you create content: in-house content creators or agencies
- when: content production schedule
Content distribution
Where do you want to distribute the content assets?
- own channels (corporate publications, corporate events, websites, blogs, company-managed online communities, online news newsletters, social media accounts, mobile notifications, and apps)
- paid channels (traditional means of advertising)
- earned channels, for example, in the form of likes, reviews, comments (include coverage and exposure that is provided by word-of-mouth or advocacy).
Content amplification
How do you plan to leverage content assets and interact with customers?
- creating conversation around content
- use of buzzers and influencers (opinion leadership have large subscriber bases and act as independent media that they trust. For opinion leaders to support and disseminate brand content, the principle of reciprocity is applied. The secret is to form and develop mutually beneficial relationships with them).
Content marketing evaluation
How successful is your content marketing campaign?
- Performance evaluation is an important step after content distribution. It includes both strategic and tactical indicators.
- content marketing metrics (5 categories of metrics: 1 – content visible (awareness); content reach and awareness; 2 – recognizable (attractiveness); how many views each visitor has, the unnecessary views rate and site visit time; 3 – searchable (question); how content can be found through search engines, search engine position metrics, and search engine links; 4- actionable (action); how well content manages to get customers to act, click-through rate and other call-to-action conversion rates; 5 – who are eager to share in social networks (advocacy) the exchange ratio and the coefficient of inclusion)
- overall objective achievements strategic indicators.
Content-marketing improvement
How do you improve existing content marketing? Since content marketing can be measured by certain metrics, you have to analyze these indicators and improve them:
- change theme
- improvement
- content distribution and amplification improvement
In the digital age, the customer path is not always easy. Marketers need to guide customers every step of the way through physical and online channels.
Omnichannel marketing
Omnichannel marketing – the technique of integrating different channels to create a seamless and consistent customer experience. It requires organizations to break down the disparity of channels and unify their goals and strategies.

Step by step omnichannel marketing
Display all sorts of the touchpoints and channels on the customer path
The touchpoints are any interaction of the user with the brand on the way of the buyer. Channels are divided into two types – communication and sales. Communication channels are ways of delivering content: advertising in social networks, publications in the media. Sales channels are a website or a dialogue with a consultant.
The touchpoints can include several types of channels.
Identifying the most important the touchpoints and channels
Any user can choose their combination of the touchpoints across multiple channels in a sequence that the authors call a “customer path scenario”. There are many scenarios for each specific product.
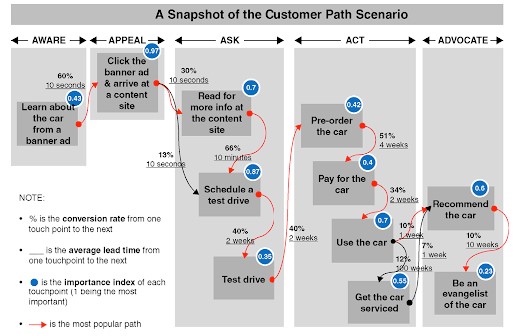
Step 3. Improve and integrate the most important the touchpoints and channels
After identifying the most critical of the touchpoints and channels to buy, you need to focus your marketing efforts on them. To help customers move from buying to brand advocacy, marketers need a series of customer engagement tactics. There are three popular techniques that have proven effective in increasing engagement in the digital age.
The first technology is the use of mobile applications to improve customer service
Use case:
- Mobile apps can act as a means for content.
- Applications can be self-service channels through which customers access their accounts or make transactions.
- Apps can be integrated into the main product or service experience.
The second technology is the application of the customer relationship management system
Social CRM is the use of social networks to manage brand interactions with customers and build long-term relationships.
The third technology is the use of gamification to improve interaction
Gamification (using the principles of the game in a non-gaming context). The essence of gamification is to reward consumers for certain actions. It is mainly used in two main contexts of engagement creation: loyalty programs and customer communities.
The three methods are not mutually exclusive. In reality, marketers have to combine them to achieve the best result.
The book “Marketing 4.0: Moving from Traditional to Digital” is a guide to explore the marketing of the new digital generation. The advent of the digital age has changed many aspects of our lives from the interaction between people to doing business in general. These changes apply to marketing as well. The authors in their book propose a new approach in marketing, which they call Marketing 4.0. The essence of Marketing 4.0 is to adopt a shift in the roles of traditional and digital marketing based on customer engagement, which should lead to brand advocacy.




